Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 08-11-2025 Origin: Site

You know that picking the right material for rubber o rings is important. The right choice stops leaks and keeps machines safe. It also helps you save money over time. When you match the material to your needs, things work better and last longer. Mingyu Sealing Technology has almost 30 years of experience. They help you find sealing solutions you can trust.
Picking the right rubber o ring material is very important. It helps stop leaks and keeps machines safe. It can also help you save money over time.
Static o rings work best for parts that do not move. Dynamic o rings are made for parts that move. Knowing this difference helps you pick the right o ring for your job.
Always think about chemical resistance and temperature range when choosing o ring materials. This makes sure the material can handle the job it needs to do.
Check dynamic o rings often for signs of wear or damage. They might need to be changed more because they move and rub a lot.
Talk to a trusted supplier like Mingyu Sealing Technology for expert help. They can give advice and custom solutions for what you need.

Rubber o rings are very important in many machines. There are two main types. One is static o rings. The other is dynamic o rings. Each type works best in certain jobs. If you know the difference, you can pick the right one for your machine.
Static o rings seal parts that do not move. You use them in pipes, covers, and flanges. These o rings last longer because they do not rub much. You can use softer materials like silicone for these. They can fail from squeezing out, swelling, or getting damaged when put in.
Tip: Use static o rings where parts do not move and pressure stays the same.
Some common static o rings are:
Buna o rings (Nitrile): These are used a lot. They are good with oil and fuel.
Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) o rings: These are also popular. They work well with strong chemicals.
Dynamic o rings seal parts that move against each other. You see them in pumps, shafts, and hydraulic cylinders. These o rings need to be tough and resist wearing out. HNBR is a good material for this. Moving parts wear out o rings faster, so you may need to change them more often.
Feature | Static O Rings | Dynamic O Rings |
|---|---|---|
Movement | No movement between surfaces | Surfaces move against each other |
Materials | Softer materials like Silicone (VMQ) | Tough materials like HNBR |
Durability | Lasts longer when not moving | Wears out faster because of movement |
Compression | Squeezed 10% to 30% because of movement | |
Design Complexity | Simple shapes | More complex shapes for moving parts |
Tolerance to Misalignment | Can handle some misalignment | Needs to fit tightly to avoid wearing out |
Heat Generation | Makes little heat | Makes heat from rubbing, needs to cool down |
Pressure Distribution | Pressure stays even | Pressure changes because of movement |
Dynamic o rings can fail from wearing out, getting hard from heat, or cracking. You should check these o rings often to keep machines working well.

Picking the right material for rubber o rings is important. Each material has its own strengths. You need to know how they work in different places.
Nitrile, or Buna-N, is a popular choice for o rings. It is used where there is oil, fuel, or grease. Nitrile o rings are good for hydraulic systems and car engines. They are strong and cheap. But they do not do well with sunlight, ozone, or strong chemicals.
Tip: Use Nitrile o rings for oils and fuels. Do not use them outside or with lots of chemicals.
Here is a table that shows chemical resistance:
Material | Chemical Resistance Properties | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Nitrile (Buna-N) | Works okay with oil, fuel, and grease. Does not do well with sunlight or weather. | Not good for strong chemicals or acids. |
FKM (Viton®) | Handles many chemicals, even strong acids. | Better for tough chemical places than Nitrile. |
Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR) | Handles heat and fuel better than regular Nitrile. | Works better in some jobs. |
Aflas® | Good chemical resistance in some jobs. | Good for very tough chemical places. |
Fluorosilicone | Good chemical resistance in some jobs. | Good for jobs with strong chemicals. |
Viton, or FKM, is a strong material for o rings. You use Viton when you need to fight chemicals and heat. Viton o rings are used in chemical plants, cars, and planes. They handle acids, fuels, and cleaners better than Nitrile.
Here is a table that shows how hot or cold Viton can get:
Source | Temperature Range |
|---|---|
Barnwell | -20°C to +205°C (up to +230°C for short times) |
Allied Metrics | -15°F to 450°F (up to 527°F for short times) |
Apple Rubber | -13°F to 446°F |
Global O-Ring | -15°F to 450°F (higher for special types) |
Note: Viton o rings are great with heat and chemicals. Use them where other o rings might fail.
EPDM o rings are best for outside jobs. You see EPDM in building, cars, and water pipes. EPDM does not break down in sun, rain, or bad weather. It is a good choice for seals that stay outside.
EPDM works well outside, even with sun and rain.
Inside, you may not need EPDM, so other materials can work.
EPDM is made to last, so it is good for outdoor jobs.
Silicone o rings are safe for food and medicine. You use silicone when you need a seal that does not react. Silicone can take high heat and many chemicals. It does not mix with food or medicine, so it is safe to use.
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Non-toxic | Safe for things people use and for medical tools. |
Temperature Resistance | Can take high heat, good for cleaning. |
Chemical Resistance | Handles acids, bases, water, oil, and fungus. |
Silicone o rings do not react with other things.
They are safe for use with people and food.
You can use them in medicine, food, and drug making.
Neoprene o rings are used in fridges, cars, and some chemical jobs. Neoprene fights oil, some chemicals, and weather. It costs less than Nitrile, but does not last as long with lots of oil.
Cost Tip: Nitrile o rings cost more than Neoprene because they last longer with oil. If you use a lot of oil, Nitrile may save money later.
Some jobs need special o rings. These include FFKM, PTFE, HNBR, and Aflas®. You use these in chemical plants, planes, and other tough places.
FFKM o rings work with many chemicals and high heat.
PTFE fights most chemicals and works in hard places.
HNBR is better with rust and heat, good for cars and planes.
Aflas® and Fluorosilicone are for special chemical needs.
Material | Properties |
|---|---|
Fluoroelastomer (FKM) | Great at fighting chemical damage, good for strong acids and cleaners. |
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Does not react with most chemicals, good for tough jobs. |
Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Handles oil, acid, and air damage, good for some chemicals. |
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Better with rust and heat, good for cars and planes. |
FFKM O-rings | Works with many chemicals, stays strong in hard places. |
You find special o rings in oil plants, drug making, food factories, planes, and cars. They stop leaks and keep machines safe in hard jobs.
When you pick O ring materials, you should think about four things. These are chemical resistance, temperature range, durability and wear, and cost. Each one changes how well your seal works in different places.
Chemical resistance means how well an O ring can handle oils, fuels, acids, and cleaners. If you use the wrong material, the O ring might swell, crack, or break. You must choose a material that matches the chemicals in your system.
Tip: Always look at the chemical compatibility chart before picking an O ring for oil and gas work.
Here is a table that shows how some materials handle chemicals:
Rubber Material | Chemical Compatibility | Rating Legend |
|---|---|---|
Nitrile | Oil, Fuel | 1 (Satisfactory) |
EPDM | Water, Steam | 2 (Fair) |
Viton (FKM) | Acids, Solvents | 1 (Satisfactory) |
Neoprene | Mild Chemicals | 2 (Fair) |
Silicone | Food, Medical | 3 (Doubtful) |
If you use strong acids or solvents, Viton is a good pick. For water and steam, EPDM works best. Nitrile is great for oil and fuel. Always check the rating before you choose.
Temperature range tells you how hot or cold an O ring can get before it stops working. If you use a seal outside its range, it can get hard, crack, or lose its shape. You need to know the limits for your job.
Here is a table with the highest temperatures for common materials:
Material | Maximum Operating Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|
Nitrile (NBR) | 275 |
EPDM | 300 |
Viton (FKM) | 400 |
You can see that Viton can take the most heat. EPDM is good for hot water and steam. Nitrile works for most oils but does not like high heat.
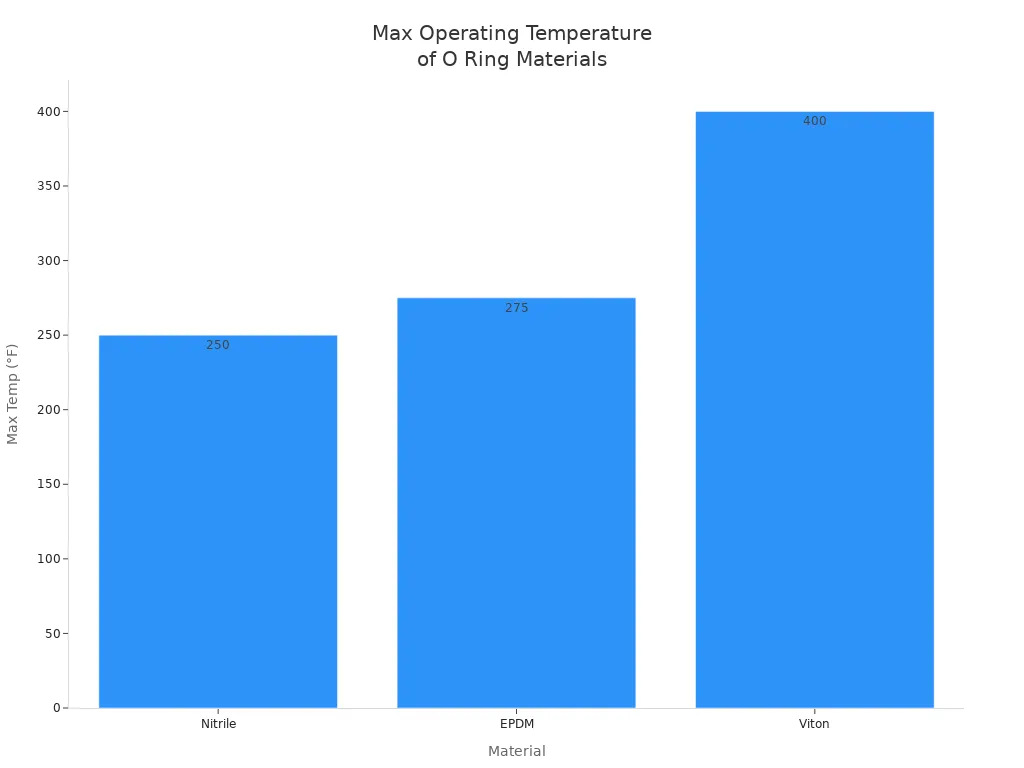
Note: Always check both the lowest and highest temperature ratings for your O ring material.
Durability means how long an O ring lasts before it wears out. Wear happens when the O ring rubs on moving parts or faces pressure changes. If you pick the right material, your seal lasts longer and you do not have to change it as much.
Polyurethane is tough against rubbing, tearing, and squeezing out. You can use it in jobs with lots of movement.
FKM and HNBR are good in places with high heat and chemicals. They stay strong in hard jobs.
Common ways O rings fail include:
Rubbing from friction
Losing bounce after being squeezed
Swelling or cracking from chemicals
Stretching too much or putting it in wrong
Damage from heat or chemicals in the air
Tip: Check your O rings often if they work in moving parts or tough places.
Cost factors help you plan how much you spend on seals. The price of O rings depends on many things.
Order Volume: Buying more at once makes each O ring cheaper, but you need to watch your money.
Custom Specifications: Special sizes or materials cost more. Standard sizes are cheaper.
Certifications: If you need special papers or checks, the price goes up.
Supplier Location: If your supplier is close to shipping places, you get your order faster and with fewer mistakes.
Payment Terms: How you pay can change the total cost and who pays for shipping.
Tip: Work with a trusted supplier like Mingyu to get the best price and help for your sealing needs.
When you look at these four things, you can pick the best rubber o rings for your job. This helps your machines last longer and stay safe.
A table can help you pick the best rubber o ring material. It lets you see how each one is different. You can check things like price, how long it lasts, and if it can handle heat or chemicals. This makes it simple to find what works for your job.
Here is a table that shows important facts about common rubber O ring materials:
Metric | Nitrile (Buna-N) | Viton (FKM) | EPDM | Silicone | Neoprene | Specialty (FFKM, PTFE, HNBR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Relative Cost | Low | High | Medium | Medium | Low | Very High |
Compression Set | Good | Excellent | Good | Fair | Good | Excellent |
Resilience | Good | Good | Excellent | Good | Good | Excellent |
Tear Strength | Good | Good | Fair | Fair | Good | Excellent |
Heat Aging | Fair | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Ozone Resistance | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Oil & Grease Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Poor | Poor | Good | Excellent |
Fuel Resistance | Good | Excellent | Poor | Poor | Fair | Excellent |
Water Swell | Fair | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
Gas Impermeability | Good | Excellent | Good | Fair | Good | Excellent |
Abrasion Resistance | Good | Good | Fair | Fair | Good | Excellent |
Temperature Ranges (°F) | -40 to 275 | -15 to 450 | -60 to 300 | -75 to 450 | -40 to 250 | -65 to 600 |
Tip: Use this table to see which material fits your needs. Think about things like heat, chemicals, and if parts move. You can also check how long you want the seal to last or how easy it is to put in.
Engineers use tables like this to match the material to what it will touch, the heat, and the pressure. You should also think about the shape of your parts and if they move a lot. This helps you choose a material that will last longer and work better.
If you are not sure what to pick, Mingyu Sealing Technology can help you. They can show you the best choices for your job.
If you work where it gets very hot, you need special O rings. Some O rings can stay strong and keep their shape in high heat. Look at this table to see which ones are best for hot jobs:
Material | Max Temperature (°C) | Max Temperature (°F) | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
CSM | 150 | 300 | Stays strong in dry heat, sunlight, ozone, and harsh chemicals. |
EPDM | 170 (short-term) | 338 | Good against cuts, steam, and squeezing. |
HNBR | 150 | 300 | Very strong and stretches well. |
Silicone Rubber | 305 | 580 | Works well even in very high heat. |
FKM | 220 (continuous) | 430 | Keeps its stretch and fights chemicals. |
FFKM | 325 | 617 | Best for super hot and tough chemical places. |
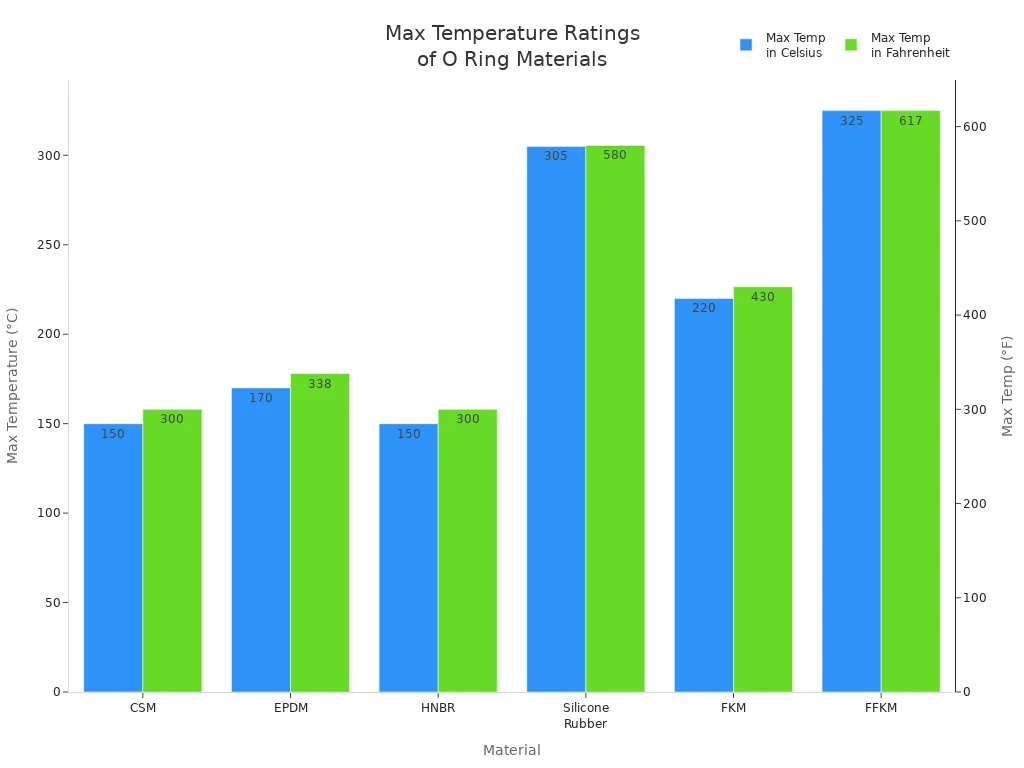
Silicone and FFKM can take the most heat. Pick these for ovens, engines, or places with lots of chemicals.
In chemical plants, O rings touch strong acids and cleaners. FKM and FFKM are good because they do not break down with chemicals. EPDM is good for water and steam, but not for oil. Always pick an O ring that matches the chemicals you use.
Tip: For strong acids or cleaners, use FKM or FFKM. They last longer and keep you safe.
O rings for food and medicine must be safe and clean. Pick O rings that follow these rules:
Safe for food by FDA rules.
Safe for the body by USP Class VI.
Made in clean factories.
Pass tests for water and oil safety.
Class I for cooking oils and milk, Class II for water and drinks.
Silicone and EPDM are used a lot here. They do not mix with food or medicine.
O rings outside get sun, rain, and ozone. Some O rings crack or get hard in sunlight. Nitrile does not last long outside. Silicone and fluorocarbon do not break in the sun. EPDM is best for ozone and weather. Use EPDM or fluorocarbon for outdoor jobs.
Most machines need O rings that last and do not cost a lot. Nitrile works for oil and water. Viton is good for heat and chemicals. Neoprene fights sun and weather. Here is a simple chart:
Material | Temperature Range | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
Nitrile (Buna-N) | -35°F to 250°F | Good for oil, water, and most jobs | Cars, boats, machines |
EPDM | -60°F to 250°F | Good for steam, water, and weather | Hydraulics, outside, brakes |
Viton (FKM) | -15°F to 400°F | Handles heat and chemicals | Engines, fuel systems |
Neoprene | -40°F to 450°F | Fights weather, cuts, and bending | Fridges, air conditioners |
You can use rubber o rings in many places. Always pick the right material for your job to get the best results.
Picking the right material for rubber o rings keeps machines safe. It also helps them work well for a long time. You can follow some easy steps to make a good choice.
Identify the functional goals. Think about what you want the o ring to do. Does it need to seal, stop shaking, or hold pressure?
Analyze the environment. Check if the o ring will face heat, cold, chemicals, or weather outside.
Work with a trusted supplier. If your job is special, talk to a company like Mingyu. They can help you pick the best material and design.
You should look at some important things before you pick a material. The table below shows what you need to think about:
Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
Chemical compatibility | Make sure the material can handle the chemicals it will touch. |
Compression set and tension set | See how the material acts when squeezed or stretched. |
Stress relaxation | Check if the material keeps sealing over time. |
Thermal resistance | Find out if the material can resist heat without breaking down. |
Cold temperature resilience | Make sure the material works in low temperatures. |
Abrasion / wear resistance | Pick materials that can handle rubbing and wear. |
Tear resistance | Choose materials that do not tear easily. |
Coefficient of thermal expansion | Know how much the material grows or shrinks with temperature changes. |
Compressibility | See how much the material compresses under load. |
Tip: Always match the o ring material to your job and where it will be used. This helps stop leaks and keeps machines from breaking.
If you have a hard job or need something special, ask Mingyu for help. Their experts can help you choose and get the right rubber o rings for your needs.
When you pick the right rubber o rings, machines work better. They last longer and do not break as fast. Each material is good for certain jobs. Look at this table to see which ones fit best:
Material Type | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Viton® (FKM) | Handles chemicals and heat well | Used in chemical plants and cars |
Silicone | Bends easily and is safe for people | Used in food and medical tools |
Neoprene | Stays strong in sunlight and ozone | Used outside and in fridges |
Mingyu Sealing Technology has important safety certificates. Their team knows a lot about seals. You can count on them for good products and help. Pick Mingyu for your next sealing job.
You should choose silicone or FKM (Viton) for high heat. These materials stay strong and flexible when temperatures rise. They work well in ovens, engines, and chemical plants.
Check what your O ring will touch, like oil, water, or chemicals. Look at the temperature and pressure. Use tables in this guide or ask Mingyu experts for help.
You should use EPDM or silicone for outdoor jobs. These materials resist sunlight, rain, and ozone. For indoor jobs, nitrile or neoprene often work well.
You need to check O rings during regular maintenance. Replace them if you see cracks, swelling, or wear. Dynamic O rings may need changing more often than static ones.
Yes! Mingyu can design and produce custom O rings for your special needs. You can contact their team for expert advice and fast service.